 NATURAL CAPITAL
NATURAL CAPITAL
Committed to environmental stewardship
TATA Group Commitment
As the Tata group sets bold targets on environmental sustainability, our businesses are not only aligned to India’s vision of sustainability and climate change but are also at the forefront of the massive global effort aimed at combating climate change and bringing about more environmentally responsible growth.
The Tata Sustainability Group (TSG) serves as a Centre of Excellence and nodal resource on sustainability for Tata Group of companies. TSG embeds sustainability into our business strategies and transition them to a low-carbon scenario. Tata Projects is well aligned with the Group’s mandate to reduce India’s energy imports and enhance national self-reliance by repurposing waste and under utilised local renewable carbon resources.
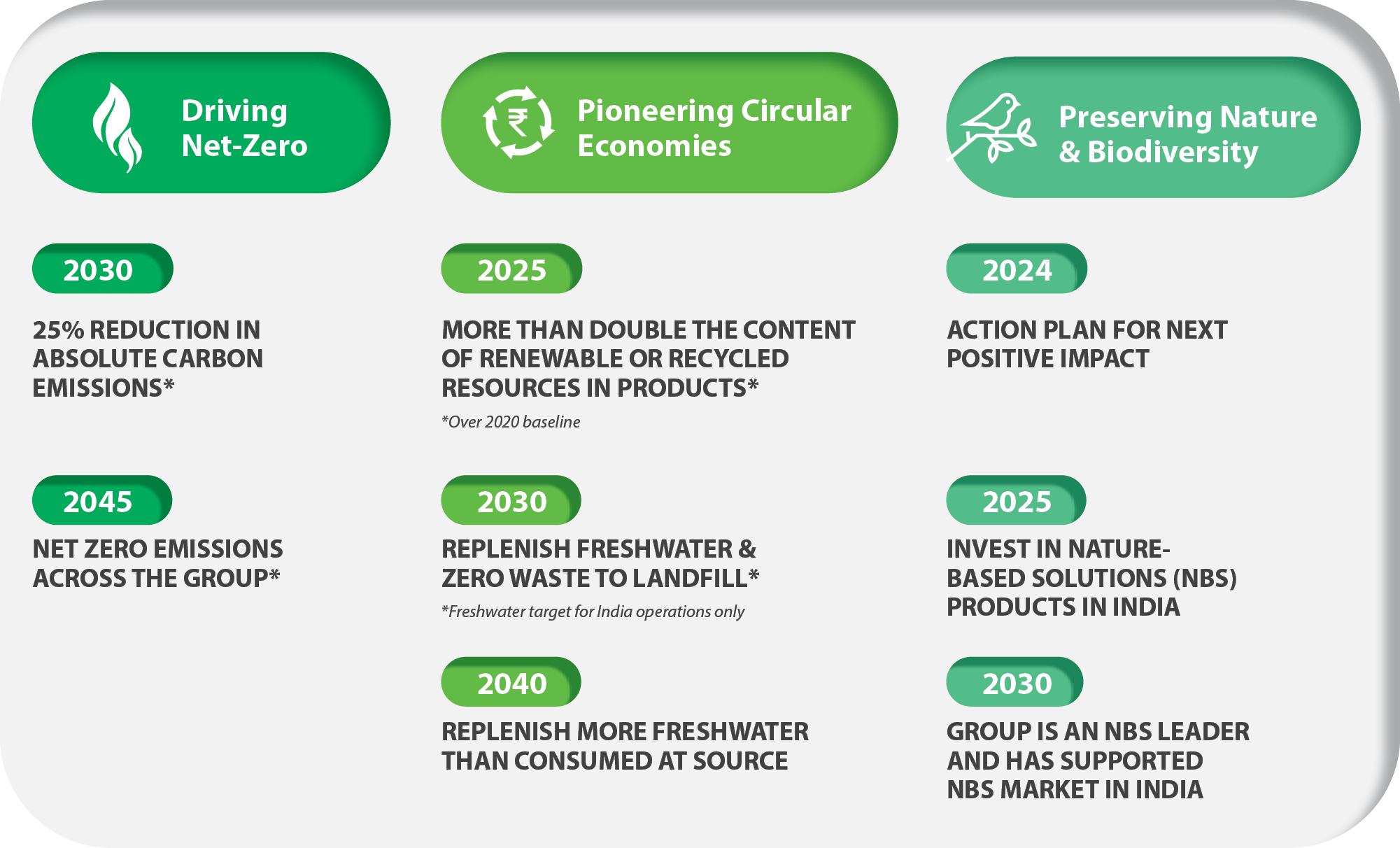
With Tata Group’s ‘Project Aalingana’, we are committed to our sustainability goals, embracing the Group’s vision for a greener, cleaner, and more equitable future. This project outlines Tata Group’s approach towards planet resilience, striving for Net Zero by 2045 and securing the future through innovative solutions. The project commits to embed sustainability into our business strategy by focusing on three inter-connected pillars.
Project Aalingana commits to embedding sustainability into business strategy by focusing on three interconnected pillars

Our Commitment to Environmental Stewardship
As a leader in India’s construction and infrastructure sector, Tata Projects is committed to its business responsibility. Our business vision pursues the triple bottom line approach while conducting business socially, economically, and environmentally to benefit current and future generations. Environmental responsibility and social commitment are taken into account in addition to our economic performance as we approach sustainable growth. We have embraced construction practices that are sustainable, ensure judicious use of natural resources, minimize the impact on the environment, and safeguard the eco-system.
Natural capital represents all the renewable and non-renewable resources that we utilise for our operations, including raw materials, land and water. We make these investments to ensure that our operations are sustainable.
At Tata Projects, to translate our sustainability initiatives into lasting outcomes, we proactively reduce our environmental footprint and focus on environment conservation and optimise the use of natural resources – thus contributing meaningfully to the fight against climate change.
Key Numbers in FY2023
96%
LED Lighting Used Across Projects
100%
LED Lights Used in Office Locations
2,79,147 KL
Water Saved
5,068 GJ
Renewable Energy Consumed
36,183
Saplings Planted
Our Key Areas of Focus
In line with the Tata Group sustainability initiatives our key focus remains
- Resource Efficiency
- Climate Change
- Water
- Bio-diversity
At Tata Projects, we provide sustainable solutions for executing large and complex urban and industrial infrastructure projects. We leverage our domain knowledge across business segments to address the shift to clean energy to meet the nation’s net zero ambitions.

Our Approach to Sustainability
Our Infrastructure Decarbonisation Strategies
Redesign. Reduction. Reuse.
Redesign involves optimising infrastructure design and construction methods to improve energy efficiency and reduce carbon footprint. It also involves redesigning infrastructure to optimise material consumption, change the material mix, use alternate building materials, such as use of Msand, Micro silca, Slag cements, and Flyash/GGBS.
Reduction involves a reduction in material consumption and wastage. This is done by adopting 3D engineering tools like Building Information Modelling (BIM), increasing precast, pre-fabrication, and use of pre-fabricated structures for temporary facilities like site offices, store, labour colony, and security cabins, and use of renewable energy in area lighting, among other things.
Reuse involves recycling building materials and other resources used during construction. This can mean recycling construction waste such as concrete, steel, paper, e-waste.
Governance Model for ESG Management
- Board level: CSR and ESG Committee
- Management level: ESG Committee
- ESG Champions
ESG committee looks into the areas including, but not limited to,
- Emissions: Energy Management
- Green Portfolio
- Waste and Circular Economy
- Water and Effluents, Biodiversity and Noise Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Employee Management and Development,
- Human Rights
- Local Community Support
- Occupational Health and Safety
- Product Safety and Quality
- Sustainable Supply Chain
- Business Ethics and Compliance
- Digitalisation, and Innovation
- Risk Management
- Business Continuity
- Sustainable Corporate Governance
Measuring the Impact
Water Consumed (KL)
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 27,05,071 | 39,07,577 | 35,02,527 | 42,47,603 |
Water Recycled (KL)
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 63,881 | 37,750 | 1,62,424 | 2,46,845 |
Using Different Materials and Recycled Input Materials in Our Operations
| Raw material | UOM | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | Cum | 86,718 | 38,483 | 95,794 | 99,706 |
| GGBS | Cum | 33,315 | 33,035 | 83,668 | 1,06,192 |
| Fly ash bricks | No’s | 79,94,308 | 56,64,644 | 1,69,81,982 | 94,83,140 |
| AAC blocks | Cum | 3,02,110 | 78,235 | 4,29,303 | 28,320 |
| M Sand | Cum | 3,18,052 | 3,85,250 | 5,81,387 | 7,30,960 |
| Micro Silica | Cum | 18,182 | 14,635 | 39,344 | 28,868 |
Recycling of Waste to reduce dependency on Natural Resources
Hazardous waste is transported as per the statutory requirements and waste management methodologies. This includes spent oil, oil-soaked cotton waste, used chemical, paint sludge, oil containers, batteries, e-waste paint residues, zinc and Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) Sludge is disposed of through Government approved recyclers and re-refiners. The Electronic waste (e-waste) is disposed off through authorised vendors, as per the statutory requirements and waste management methodologies. The biomedical waste generated at dispensaries and health centres is disposed off as per statutory requirements and responsible disposal is ensured. We do not import, export, transport or treat any hazardous waste. Office waste papers are disposed through ITC WOW Disposal initiatives.
Steps Taken to Enable the Shift to Alternate Energy
Tata Projects have been in the forefront of using Renewable Energy at our sites located in the different corners of the country. Our usage of RE power has grown substantially over the years .
We have also taken on priority usage of LED lights at all our sites with an aim to moving to 100% usage of lowest energy consumption lighting solutions at our facilities
Renewable Energy Consumption - Solar Energy (GJ)
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,055 | 714 | 2,089 | 5,068 |
Use of LED Lights (%)
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 72 | 73 | 87 | 96 |
Year-on-Year Energy Consumption (GJ)
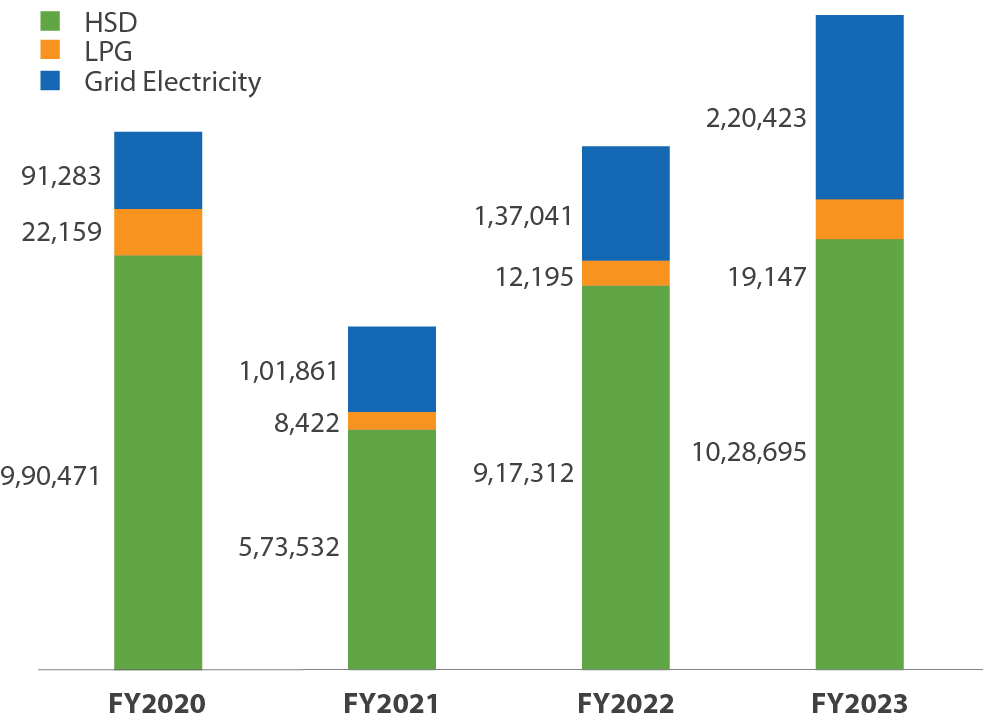
Emissions (tCO2e)

Energy Saving (MWH)*
| S.No | Project | FY2018 | FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pune LED | 20,184 | 37,101 | 40,766 | 40,907 | 40,868 | 41,793 | 2,21,619 |
| 2 | Noida LED | - | - | 16,034 | 30,353 | 30,542 | 30,542 | 1,07,471 |
| 3 | Ludhiana LED | - | - | 1,102 | 20,691 | 32,664 | 24,557 | 79,014 |
| 4 | Nashik LED | - | - | - | 10,070 | 34,704 | 38,864 | 83,638 |
| Total Cumulative Energy Saving on Yearly basis in MWH | 20,184 | 37,101 | 57,902 | 1,02,021 | 1,38,778 | 1,35,756 | 4,91,742 | |
* Estimated based on baselining and Replaced LED watts + running hours
In sectors where we have a presence, we are planning to enter into adjacencies such as battery energy storage projects and battery manufacturing, and setting up data centres. We are working on moving vehicles and equipment from diesel to cleaner energy sources to ensure lower emissions and a more sustainable future for the sector and the planet.
As part of Tata group’s commitment to the planet, the shift to cleaner alternate energy remains at our core. We are looking at continuous collaboration between academia and industry to find innovative pathways towards that goal.
We take pride in partnering with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-Indian Institute of Petroleum (CSIR-IIP), as part of our efforts to Decarbonise our construction sites, one of Tata Project’s pioneering step in addressing the Sustainability related challenges of the hard to-abate construction industry.
Indigenous state-of-the-art technology solutions, like converting waste cooking oil to bio-diesels, have already been initiated into our sites. We are presently evaluating the conversion of site-generated organic waste to bio-gas and the use of 100% replaceable Green Diesels in our construction equipment as the next step. We are also exploring the utilisation of the green diesel by-product from the DILSAAF™ (Drop-In Liquid Sustainable Aviation Fuel and Automotive Fuel) pilot plant.
Tata Sustainability Month
We encourage employee and stakeholder engagement in our sustainability initiatives. Tata Sustainability Month (TSM) is celebrated each year. During this period of celebration, our employees participate in several initiatives on sustainability, biodiversity, plantation drive and SMART connections, along with quiz competitions and pledges. During the year, we collaborated with Tata Sustainability Group (TSG) and our internal stakeholders, and enrolled 3,139 of our employees for the initiative.
Tata Projects was ranked 1st in the Tata Group for enrolment in the Sustainability Champions course, which also helped us earn recognition from the TSG Chairman.
In FY2023, a specially designed e-course curated by sustainability experts was offered to Tata Group employees. This was a unique opportunity to learn about sustainability and adopt cleaner, greener lifestyles through an exclusive e-course titled ‘Only one Earth’ (in alignment with the United Nations World Environment Day theme). The power-packed e-course distilled years of sustainability knowledge into 19 micro-modules and was made available to all the Tata Group employees throughout June and completion certificates were provided to these employees.
Sustainability Initiatives
 During the construction of the New Parliament Building, a key challenge faced was to minimise generated wastewater, prevent water pollution, reduce consumption of potable water and combat dust pollution by using treated wastewater. A sewage treatment plant was installed which engaged Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) technology for effectively controlling biological aspects. We also installed a Reverse Osmosis (RO) plant for the usage of RO-rejected water.
During the construction of the New Parliament Building, a key challenge faced was to minimise generated wastewater, prevent water pollution, reduce consumption of potable water and combat dust pollution by using treated wastewater. A sewage treatment plant was installed which engaged Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) technology for effectively controlling biological aspects. We also installed a Reverse Osmosis (RO) plant for the usage of RO-rejected water.
Going forward, based on our estimate of the manpower strength needed for the project, we are estimating and creating water cycle input for usage and disposal. We are also looking at futuristic technologies such as the use of ultraviolet disinfection units to kill the remaining harmful bacteria in water.
New Parliament Building: Discharged Water Recycled (KL)
| Area | Quantity |
| Sedimentation Tanks | 1,000 |
| STP | 44,091 |
| RO Treatment | 3,835 |
| Total Water Recycled | 48,926 |
| Overall: Water Saved through Various Initiatives (KL) | |
| Water Reducing Admixture | 860 |
| Total | 49,786 |
Creating an Impact
Water Saving
98% of discharged wastewater was recycled and reused
49,786 KL water was saved in FY2023
Economic Saving
An amount of ₹ 2.48 Cr was saved by reducing the consumption of potable water for dust control and construction, and by replacing the demand for potable water with treated water.
The Shift to Renewable Energy
Tower Manufacturing Unit, Nagpur
 After having successfully implemented Renewable Energy towards manufacturing of tower parts, Tata Projects added a strong green portfolio feather to its cap. The Tower Manufacturing Unit (TMU) at Nagpur, Maharashtra, caters to most of the structural steel requirements of Transmission & Distribution segment, making it one of the most integral part of the business of Tata Projects. With an objective of making our Tower Manufacturing Unit (TMU) sustainable and with zero emissions, in January 2022, we installed solar panels and successfully commissioned them. The rooftop installation is also an efficient way of space utilization. It is estimated that the project will reduce emission of around 1,082 tCO2eq.
After having successfully implemented Renewable Energy towards manufacturing of tower parts, Tata Projects added a strong green portfolio feather to its cap. The Tower Manufacturing Unit (TMU) at Nagpur, Maharashtra, caters to most of the structural steel requirements of Transmission & Distribution segment, making it one of the most integral part of the business of Tata Projects. With an objective of making our Tower Manufacturing Unit (TMU) sustainable and with zero emissions, in January 2022, we installed solar panels and successfully commissioned them. The rooftop installation is also an efficient way of space utilization. It is estimated that the project will reduce emission of around 1,082 tCO2eq.
Preservation of Mangroves and Biodiversity
 The Mumbai Trans Harbour Link (MTHL) site, which is India’s longest sea bridge, aims to connect the satellite city with the mainland Navi Mumbai. It envisages the construction of a temporary access bridge in the inter-tidal zone to reduce disturbance in mangroves and mudflats.
The Mumbai Trans Harbour Link (MTHL) site, which is India’s longest sea bridge, aims to connect the satellite city with the mainland Navi Mumbai. It envisages the construction of a temporary access bridge in the inter-tidal zone to reduce disturbance in mangroves and mudflats.
a. Restoration of Uprooted Mangroves
The use of state-of-the-art technology Reverse Circulation Drilling (RCD) for piling and the muck generated on mudflats during piling was collected and disposed at approved locations. This led to the growth of new mangroves, helped replenish uprooted mangroves and conserve flora and fauna. Also, there was no waste disposal in the inter-tidal zone.
b. Ensuring the Count of Flamingos
No oil and chemical spillage at the intertidal and marine zone and noise limits maintained as per Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) limits ensured the flamingo count doesn’t drop. Further, twelve 12 of migratory and four species of resident birds were observed frequently in the intertidal and marine zone.
Going forward, we are ensuring muck collection in the inter-tidal zone using muck collection tanks, transportation and disposal of muck using grab and dumpers to designated disposal locations, and using muck collection tanks for the first time in inter-tidal zone piling. We also ensure the conservation of mudflat for optimal growth of Green-Blue Algae and reduce noise pollution.
Contribution in Green Environment and improvement of Citizen Services
Streetlights in a city are one of the key essential citizen services required for safe streets at night, helping to flourish business and recreation activities at late hours. This has a direct impact on economic activities and quality of life in the city. City streetlights are managed by the Local Urban Body (ULB), which is commonly constrained with financial resources. Budget constraints at ULB results into poor upkeep of streetlights apart from high energy cost due to conventional light fixtures.
ESCO Company Funded PPP Projects for ULBs / Municipal Corporations
Energy Saving Company (ESCO) takes up project under PPP model through a SPV, where it invests into replacing conventional streetlights with energy efficient Smart LED lights and recover the cost from energy savings achieved. These lights are monitored and controlled from an Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC). Such streetlights maintenance is also undertaken by ESCO for the next 7 to 10 years after upgrade of infrastructure. Presently, we are maintaining streetlights in the cities of Pune, Nashik, Ludhiana and Noida cities totaling 4 Lakh streetlights.
Reduction of Carbon Footprints
These projects have achieved energy savings in range of 56 to 62% (electrical energy is saved to the tune of 4,89,600 GJ per year). The saving is shared between the respective Local Body and the ESCO. This brings additional earning to the Local Body from saved energy cost plus annual maintenance cost of electrical fixtures and network. Since these projects have gone live and operation & maintenance phase is initiated, cumulatively these have saved 17,71,200 GJ equal to a Carbon Credit of 4.63 Lakhs till date. Over the lifecycle operations period of these projects would be equivalent to 11.28 L Tons of CO2 emission reduction.
Sustainable Operations with Municipality Cost Saving resulting into saving of over ₹12.5 Cr annually towards maintenance expenses of the city streetlights. Over the project’s lifecycle these expenses are estimated above ₹100 Cr on these four cities’ projects.
Green Thumb Initiative
The sustainability portfolio is driven by the Green Thumb Initiative, an initiative to enhance the green cover across the country. Through this initiative, we are creating awareness about our environment conservation efforts and communicating our values. Tata Projects is sensitive towards biodiversity and the environment in which it operates and takes utmost care to protect the same. Since the past few years, over 4.5 lakhs saplings have been planted by Tata Projects at its various project sites.
Key Objective
- To help restore India’s green cover
- To arrest the adverse impact of climate change
- To plant trees at projects across India
Fostering Ecology
Our sustainability strategy is mapped to the UN SDGs and demonstrates our Company’s commitment towards the attainment of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. It is built on the pillars of Environment, Economics, People and Social.
- To avoid the emission of carbon, and to protect and restore natural habitats, saplings and trees are planted across all the project sites.
- We partnered with NGOs, gram panchayats and schools to increase the green cover.

36,183
Saplings Planted in FY2023 (Compared to 35,241 planted in FY2022)
454,239
Total Saplings Planted between FY2018 to FY2023
Adopting Miyawaki of Urban Afforestation
We have restored native forests by utilising the Miyawaki technique at our Medchal plant in Hyderabad and at Metro Line 3 project in Pune. Similarly in consultation with customers, different sites and projects have adopted the Miyawaki technique. Through this technique we accelerate the creation of a natural wild and dense forest by constructing soil, utilising native plant diversity, growing healthy saplings and planting them close together in a small area to enrich the green cover, strengthen the richness of the land and nurture biodiversity.
Medchal Plant, Hyderabad
1,077sq.ft.
Total Area Covered
377
Saplings Grown
50
Native Species Used
Tril Pune Metro Line 3 Project, Pashan, Pune
3,300sq.ft.
Total Area Covered
1,013
Saplings Grown
100
Native Species Used
Key Sustainability-Based Projects
- Flue Gas Desulphurisation Coal-based Thermal Power Plants
- SMOG Tower for Air Purification
- LED Light project
- First Solar PV module manufacture/Tata Power PV module manufacture
- Noida International Airport, Jewar
- DFCs taking off trucks from the road
- Metro projects enhancing clean public transport on electrification
Our Green Buildings
- New Parliament Building, New Delhi

- Balasaheb Thackerey National Memorial Museum, Mumbai

- Tata Electronics Factory, Hosur

- Ascendas-IT Park Gurgaon

